A1 Development of Different Theories
Behavioral management theory is an approach to human resource management that considers the individual behaviours of people at work. This includes how people are intrinsically motivated and how people interact with each other such as desire for teamwork and the reasons behind conflict.
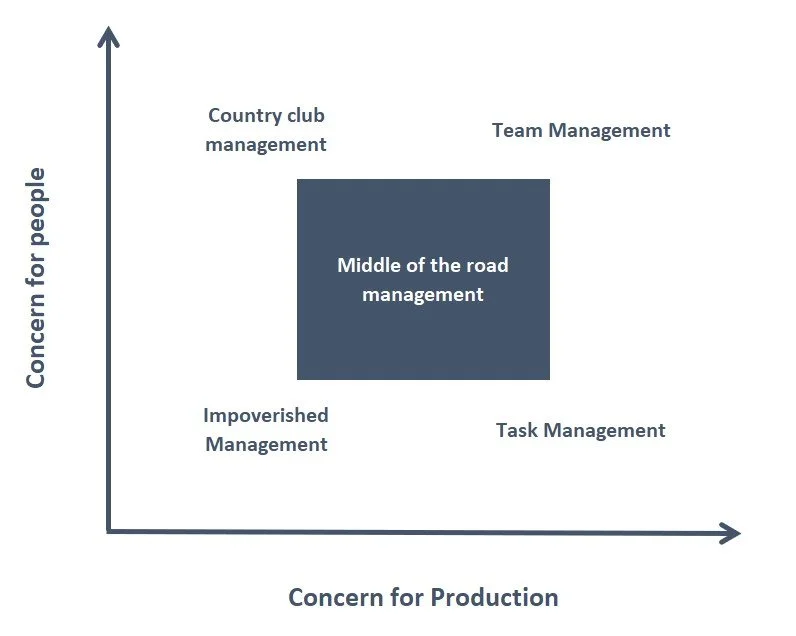
The Managerial Grid Model was a theory proposed by Blake and Mouton that managers have two behaviours, concern for the task and concern for people’s wellbeing. The degree to which they lean towards one or the other affects the result of the team.
Role theory refers to the way in which people perceive their own role and the role of others. At work this relates to how work and responsibility is split amongst employees and managers. Formal role theory refers to the policies and procedures that are set out by the organisation which clearly identify who is responsible for what. Informal role theory relates to how an individual perceives the appropriate distribution of roles. This may be influenced by culture or past experience. For example, if an employee previously worked in a team where the manager dealt with all customer complaints, they may assume that this is the case in their present role.
Situational and contingency leadership is a theory that there is not one best style of leadership but different leadership styles are more appropriate depending on the task in hand or the person the leader is working with. For example, a very Laissez-faire approach may be appropriate in the design stages of a product as people may need space for creativity. However, if there was a crisis such as a fire in that same environment, a more autocratic leadership style would be appropriate as it is safer for people to follow clear instructions. Different people feel differently about how they want to be led. Some people feel that they would like to have more freedom in their work and appreciate a laissez-faire or democratic style. However, there are people who prefer to have clear direction. It is therefore important for leaders to understand their staff and how they would prefer to be led.
Transformational and transactional leadership refers to two different styles of leadership that managers tend to take on. Transformational leadership refers to a style where leaders invest in understanding the values and motivations of their teams and find ways to present opportunities for individuals to develop their interests. For example, if a team member was passionate about the environment, the leader may give them opportunities to develop strategies for the organisation to become more environmentally friendly. Transactional leadership refers to a style where a leader establishes what their team wish to receive in return for their inputs. This may include salary or benefits such as holiday leave and medical insurance.