Business Models Used in Marketing (Unit 2 International)
Internal Factors
Every business has a different internal environment which can have an impact on their marketing decisions. Factors such as the business size, budget available, culture, values, attitudes to ethics, skills of staff and technology available will all have an impact on marketing. Firms may conduct regular audits on their internal environments to support their decisions.
External Factors
The external environment is constantly changing and while an individual firm cannot control this, it is important that they respond in order to maintain their market position. A regular STEEPLE analysis encourages in depth investigation into social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal and ethical factors in the external environment in which a business operates.
Competitor Analysis
A competitor analysis is an investigation into the activities and performance of key rivals. This can help establish a firm’s standing in the market and explore opportunities and gaps. The analysis will first identify key rivals and then their strengths and weaknesses. As competitor actions change regularly, a competitor analysis is an ongoing function of a marketing department.
Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces is a framework to support an investigation of the competitive environment of a business. It encourages a business to separately analysis the threat of new entrants, supplier bargaining power, the threat of substitutes, customer bargaining power and industry rivalry.
Product Life Cycle
The product life cycle is the stages a product goes through from development, launch, maturity and decline. Different marketing strategies are appropriate at different stages of the life cycle, e.g. informative advertising at launch, reminder advertising at maturity and discounts to clear stock during decline.
The Marketing Mix
The marketing mix is the combination of strategies used to market a product. Product strategies include quality, branding packaging and developing a USP. Pricing strategies include penetration pricing, price skimming and loss leader. Promotional strategies include cinema advertising, social media advertising and guerilla marketing. Place strategies include distribution channels such as through wholesalers and retailers.
The Extended Marketing Mix
The extended marketing mix is used in extension to the 4 Ps when selling a service rather than a tangible good. People strategies include customer service training. Process strategies include payment methods and reducing queueing time. Physical environment strategies include improving visual appeal of a hotel lobby or banking branch.
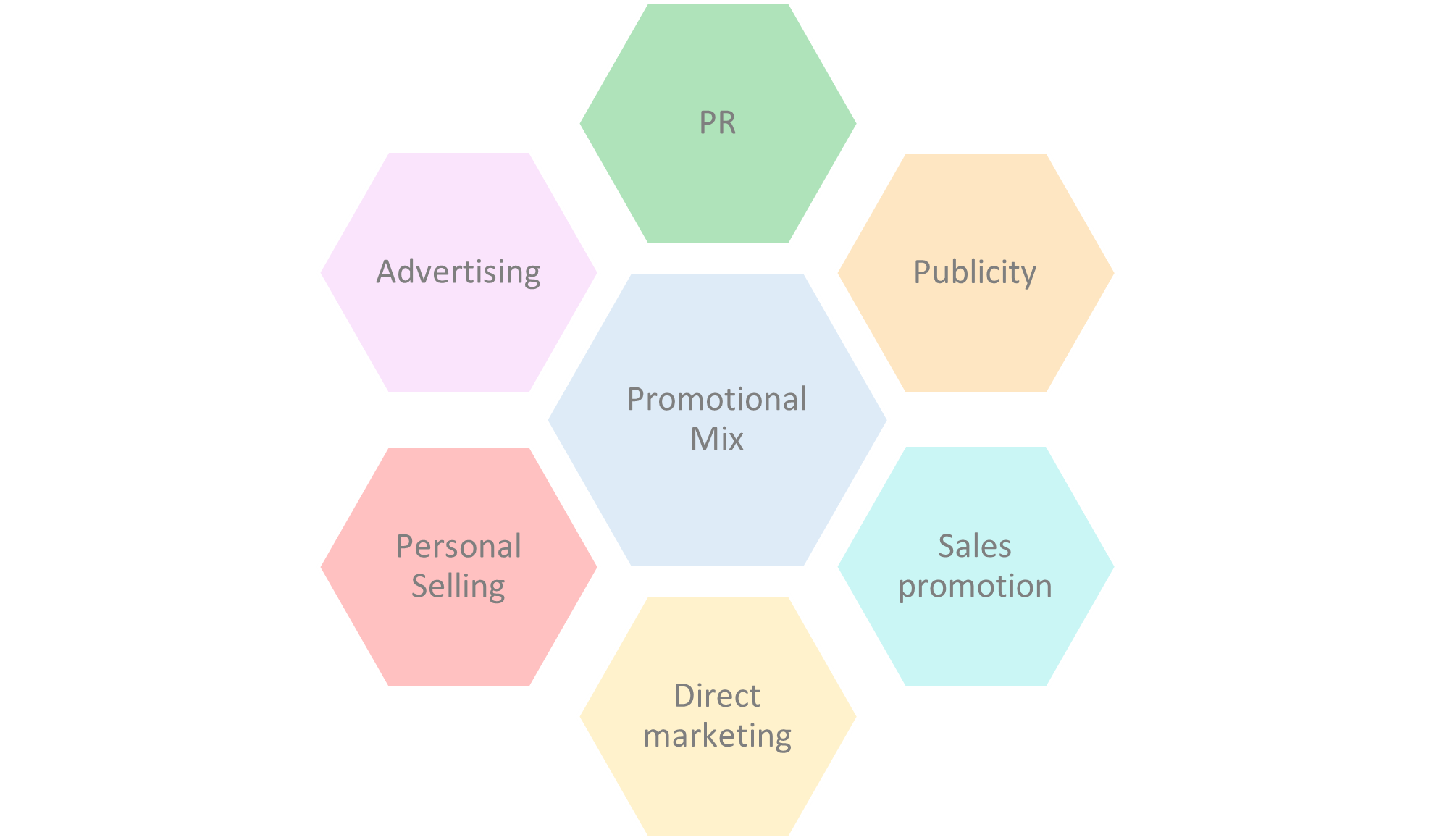
The Promotional Mix
The promotional mix refers to the range of strategies used to communicate the brand and product with consumers. Methods of promotion include advertising, PR and publicity, sales promotions, direct marketing and personal selling.
Product Positioning
A product position map compares a range of different brands in a market to establish a firm’s position in that market and identify any gaps. Any two variables can be compared, e.g. price and quality.